|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
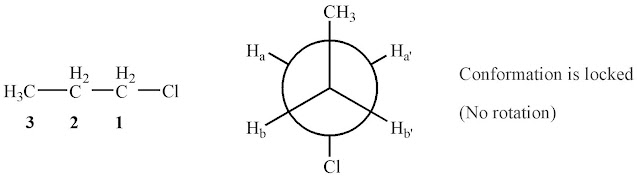
+The original Veber papers (J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615) define what they consider to be a rotatable bond: Rotatable bonds were defined as any single bond, not in a ring, bound to a nonterminal heavy (i.e., non-hydrogen) atom. Excluded from the count were amide C-N bonds because of their high rotational energy barrier.
|